Vitamin A aka Retinoids
What are Retinoids?
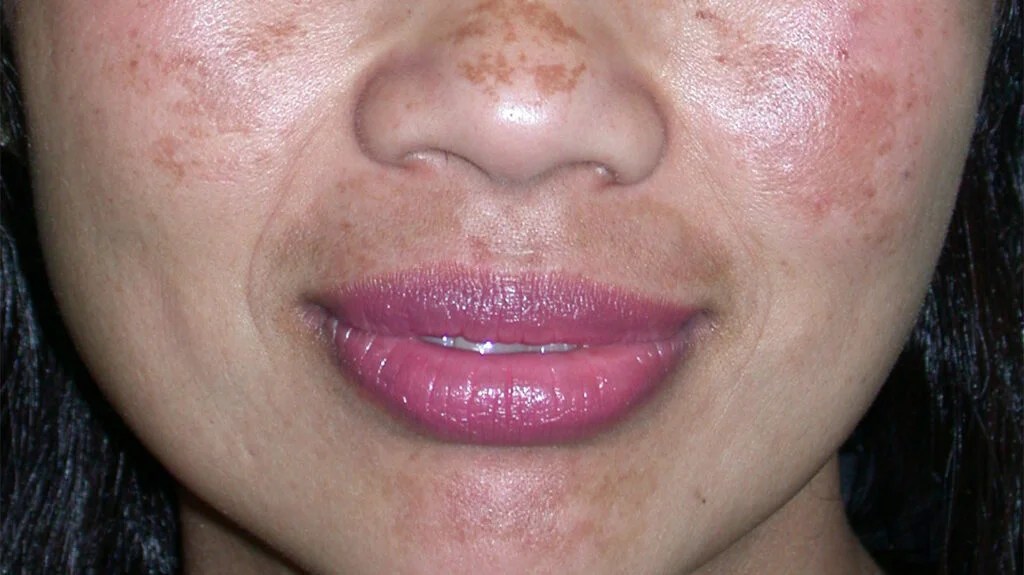
Most of us have heard of Retinol and Retin-A, but do you know that ALL retinoids and retinols are simply forms or derivitives of VITAMIN A?!
This often surprises clients when I tell them this, as Retinoids and Retinols have been vilified by some people in the skincare industry. A lot of skincare companies are making their money off of using the words “clean” and “chemical free” these days. All this does is scare the consumer. As we all know everything is a chemical, water, air, vitamins, everything. So this holds no truth and can be very unbeneficial for your skin. Vitamin A derivatives have been used for decades and have been studied since the early 20th century when the structure of Vitamin A was discovered.
Vitamin A
Our bodies can’t make vitamins, so we must get them externally. We can get vitamin A either through topical application or through the ingestion of beta-carotene-rich foods like carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach. When broken down, vitamin A and its metabolites are very beneficial. They can affect everything from vision to inflammation to the proliferation of cells.
Proliferation means growth. Retinoids increase cellular turnover in the skin, meaning they grow faster, which is going to make the skin a little bit thicker. They also make the outermost cells shed, which is why some people think it’s exfoliating, even though that’s really a secondary effect. This makes the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of skin) more compact, which gives a nice anti-aging benefit.
Unfortunatly some skincare companies such as Beauty Counter are dragging them through the mud claiming they cause cancer. This is the furthest thing from the truth and they have no clinical studies to back up their claims. We actually use retinoids to treat and prevent cancerous and pre-cancerous cells. And the clinical papers on it are never ending. Just another reason to get your skincare advice from professionals.
What does this do for me?
Retinoids also aid in the moisturization of skin by stimulating the productions of compounds that have sugars in them (glycosaminoglycans).
Most importantly they help PREVENT collagen loss and SUPPORT collagen production!
Finally, retinoids are antioxidants, so they help prevent a lot of oxidative stress. Retinoids are truly amazing and do so many great things for the skin!