What Melasma Looks Like
What is Melasma?
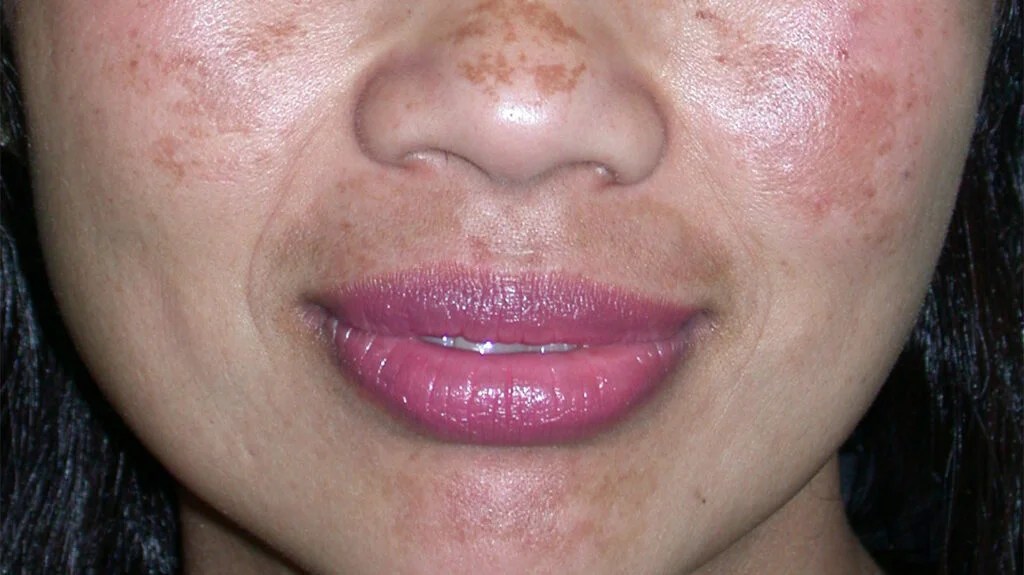
A skin condition presenting as brown patches on the face of adults. Both sides of the face are usually affected. The most common sites of involvment are the cheeks, bridge of nose, forehead and upper lip.
Who gets Melasma?
It mostly occurs in women, with only 10% of men being affected. Dark skinned races, particularly Hispanic, Asian, Indian and African American tend to experience it more than others due to the increase of melanin or pigment cells.
What causes Melasma?
The precise cause is unknown. People with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop it themselves. A change in hormonal status may trigger the condition. Melasma is commonly associated with pregnancy and also called chloasma or the “mask of pregnancy.” Birth control pills may also contribute or cause melasma, however, hormone replacement therapy used after menopause has not been shown to cause the condition.
Sun exposure is also a contributor. Ultraviolet light from the sun, and even very strong light from light bulbs, can stimulate pigment producing cells, or melanocytes, in the skin. People with skin of color have more active melanocytes than those with light skin. These melanocytes produce a large amount of pigment under normal conditions, but this production increases even further when stimulated by light exposure or an increase in hormone levels. Incidental exposure to the sun is mainly the reason for recurrences of the skin condition.
Any irritation or trauma to the skin may cause an increase in pigmentation in dark skinned individuals, which may also worsen melasma. It’s not associated with any internal diseasesor organ malfunction.
How is melasma treated?
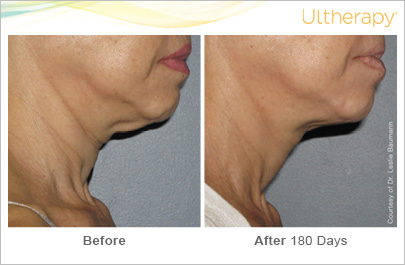
While there is no cure, many treatments have been developed. Melasma may disappear after pregnancy, it may remain for many years or a lifetime.
Sunscreen is essential in the treatment of process. They should be broad spectrum, protecting against UVA and UVB rays from the sun. A SPF of 30 or higher should be selected. In addition, physical sunblock lotions and creams such as zinc oxide and titanium oxide are preferred as they do not protect the skin in a chemical way which may cause inflammation and exacerbate the condition. SPF should be worn daily, whether or not it is sunny outside or if you are outdoors or indoors. A significant amount of ultraviolet rays is received while walking down the street, driving in cars, and sitting next to windows.
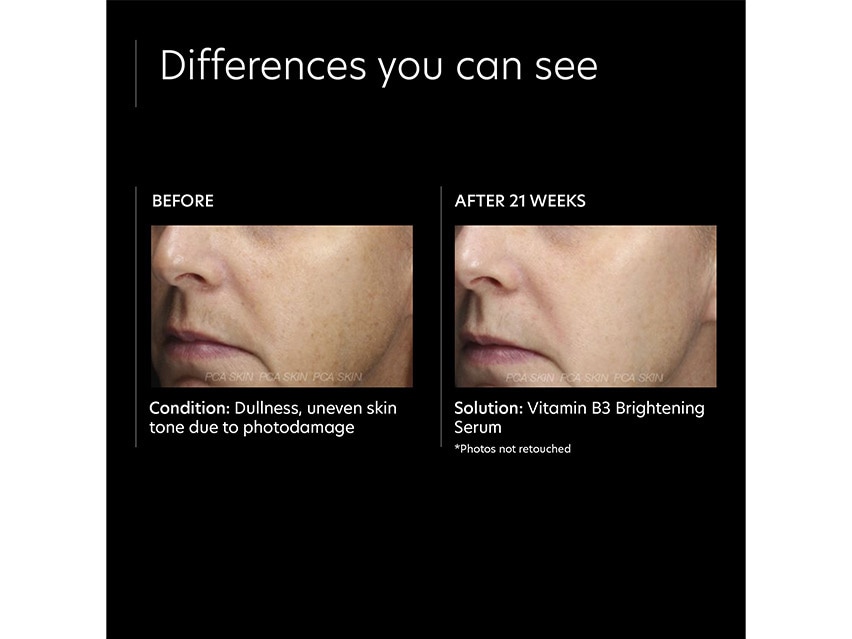
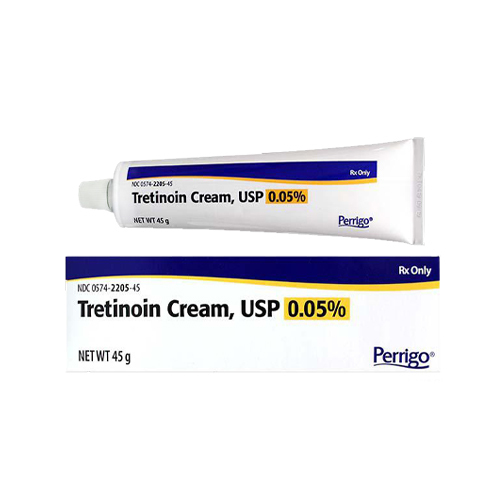
A variety of lightening creams are available for treatment. These creams do not “bleach” the skin but rather decrease the activity of melanocytes, pigment producing cells.
Other medications which have been found to help are azelic acid, kojic acid, niacinimide and Vitamin C. You will have to talk to your Dermatologist or Aesthetician to know what is right for your condition.
Chemical peels, microdermabrasion and various laser treatments may help melasma. They should only be used by a medical skincare professional and in conjuction with a proper regimen for melasma specifically.